Post Overview
- Introduction
- How it works
- Code
Introduction
I am ready to add few new features to my website, like comment, webrtc streaming and socketio real-time monitoring. They requires advanced encryption and secured connection. After some research, I was able to enable HTTPS on my site. In this blog I will demonstrate how to enable HTTPS on my setup: Nginx + Nodejs + express.
My site setup
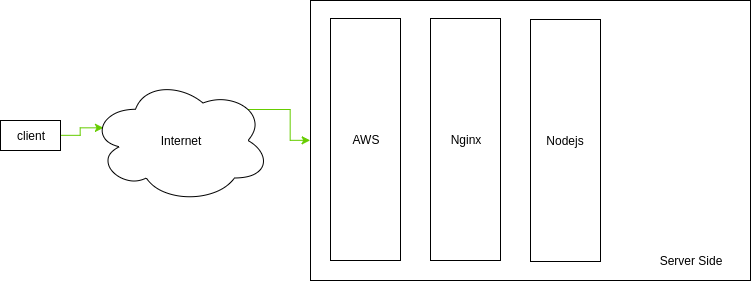
My site setup is straight forward. An AWS instance served as gate way for all the incoming connections, and all the ports
are blocked except explicitly written policies including 443 and 80 requests. The allowed requests are forwarded to
website server.
Enable HTTPS on my site
What is HTTPS
HTTPS refers to HTTP Secure, in which the communication is encrypted by TLS. We can use self signed certification or public signed certification. We will use public signed certification in my case.
What I need to do
- Allow 443 Port on AWS policy
- Get certification from one of provider
- Add pki-verification text file to server to activate certification.
- Add certification to Nginx and add 443 proxy rule to Nginx.
1. Allow 443 Port on AWS policy

2. Get certification
I did not take screenshot of this step, but it should be very straight forward.
First generate csr file in local machine with some basic information:
sudo openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 1024
sudo openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
Then filling content of server.csr to certificate provider. After that, provider instructed me to put an activation txt file in a public folder .well-known/pki-validation.
3. Add pki-verification text file

I was struggling in serving the whole folder publicly, but I found that the file can be placed in the /public folder
under the same directory name.
After couple of minutes, my site was verified and server.crt is provided. I downloaded and put this server.crt
file in the Nginx directory along with the server.key file.
4. Update nginx.conf
Last step is updating nginx conf.
We can enable HTTPS on nginx and nodejs, so I will explain both ways.
- Enable HTTPS on nginx Here is my updated nginx conf file: ``` events { worker_connections 1024; }
http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name localhost;
ssl on;
ssl_certificate /usr/local/etc/nginx/ssl/server.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/etc/nginx/ssl/server.key;
ssl_protocols SSLv2 SSLv3 TLSv1;
ssl_ciphers "HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5 or HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5:!3DES";
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Client-Verify SUCCESS;
proxy_set_header X-Client-DN $ssl_client_s_dn;
proxy_set_header X-SSL-Subject $ssl_client_s_dn;
proxy_set_header X-SSL-Issuer $ssl_client_i_dn;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_request_buffering off;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3000;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Client-Verify SUCCESS;
proxy_set_header X-Client-DN $ssl_client_s_dn;
proxy_set_header X-SSL-Subject $ssl_client_s_dn;
proxy_set_header X-SSL-Issuer $ssl_client_i_dn;
proxy_read_timeout 1800;
proxy_connect_timeout 1800;
} } ``` This is preferred way that only update nginx. The connection between nginx and nodejs is still not encrypted, but we assume that server is trusted internally.
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
This line will forward all http request to https protocol.
- Enabling HTTPS on Nginx and Nodejs
This is not necessary in common cases, but I noted here.
We first start https server in nodejs:var https = require('https'); var privateKey = fs.readFileSync('sslcert/server.key', 'utf8'); var certificate = fs.readFileSync('sslcert/server.crt', 'utf8'); var credentials = {key: privateKey, cert: certificate}; [...] var httpsServer = https.createServer(credentials, app); httpsServer.listen(3443);Then we update nginx to listen to 3443 port ``` server { listen 443 ssl; server_name localhost;
ssl on; ssl_certificate /usr/local/etc/nginx/ssl/server.crt; ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/etc/nginx/ssl/server.key; ssl_protocols SSLv2 SSLv3 TLSv1; ssl_ciphers “HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5 or HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5:!3DES”; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / { proxy_pass https://localhost:3443; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Client-Verify SUCCESS; proxy_set_header X-Client-DN $ssl_client_s_dn; proxy_set_header X-SSL-Subject $ssl_client_s_dn; proxy_set_header X-SSL-Issuer $ssl_client_i_dn; proxy_buffering off; proxy_request_buffering off; proxy_read_timeout 60s; proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
}}
**NOTE: In this case, proxy_pass should be https also but not http:**
proxy_pass https://localhost:3443; ```
Common problem
502: gateway error
I had this error for quite a long time. This error usually happened when nodejs server is not available due to the following possible reasons:
- Nodejs listens to different port number as in the nginx.conf
- proxy_pass is pointing to http but nodejs accept https request on that port
Finally
After updates above, my site is secured now!
Last update: May.30.2018